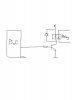
Hi. One of the technical specialists at Cypress gave me the attached schematic to communicate the CY8C24894 chip (data sheet attached) with a relay. The chip is on the PSoC in the schematic - which connects to a USB port. I’ve contacted them again asking for values for the four parts in the schematic. I’m wondering if someone might be able to answer the same question, and also take the time to explain to me what these parts are doing at these values.
Would the values of these parts likely have to be different for different chips?
Also, does anyone know of any example Java computer programs that can read analog pins on a CY8C24894 chip?
Do Java programs have to be different when communicating with different types of chips on peripherals, or can different types of chips read the same Java code?
Would the values of these parts likely have to be different for different chips?
Also, does anyone know of any example Java computer programs that can read analog pins on a CY8C24894 chip?
Do Java programs have to be different when communicating with different types of chips on peripherals, or can different types of chips read the same Java code?
Attachments
Last edited: