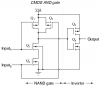
I need some query about cmos circuit
cmos circuit specification
Input voltage
output voltage
input current
output current
transistor width
transistor length
fall time
raise time
now my main problem is how do decide specification for circuit
1)Input voltage - It can be 3.3 v or 5v If its 3.3 volt then what will be output voltage ?
I think input voltage depend on output voltage and output voltage depend on input voltage that means If we know input voltage we can determine output voltage and as same for output voltage
2)how to choose transistor size for low power consumption ?
transistor size effect raise time and fall time
what will be transistor size for 100 200 300 ns ?
as rule one is known then we can determine unknown value so I am trying do this method
cmos circuit specification
Input voltage
output voltage
input current
output current
transistor width
transistor length
fall time
raise time
now my main problem is how do decide specification for circuit
1)Input voltage - It can be 3.3 v or 5v If its 3.3 volt then what will be output voltage ?
I think input voltage depend on output voltage and output voltage depend on input voltage that means If we know input voltage we can determine output voltage and as same for output voltage
2)how to choose transistor size for low power consumption ?
transistor size effect raise time and fall time
what will be transistor size for 100 200 300 ns ?
as rule one is known then we can determine unknown value so I am trying do this method