Hi, I've been studying a little about memories and I didn't understand the function of the burst feature, I guess I understood its functioning but not its importance and why is it necessary.
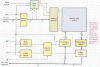
In the book says "when an external address is latched in the address register, the two lowest order address bits, A0 and A1, are applied to the burst logic. This produces a sequence of four internal addresses by adding, 00, 01, 10 and 11 to the two lowest order address bits on successive clock pulses. The sequence always begin with the base address which is the external address held in the address register.
The address burst logic in a typical synchronous SRAM consists of a binary counter and exclusive-OR gates. For 2-bit burst logic, the internal burst address sequence is formed by the base address bits A2 to A14 plus the two burst address bits A0' and A1'".
I can see that the four possible states (assuming that A0 and A1 are both 0, LOW) will be sequentially added to the external base address, but what is the point of that? I didn't see where did it say it. It says "this allows the memory to read or write at up to four locations using a single address", but what is the advantage of that?
How do they do if they only need to write or read in only a memory location?
Attached the two images.
In the book says "when an external address is latched in the address register, the two lowest order address bits, A0 and A1, are applied to the burst logic. This produces a sequence of four internal addresses by adding, 00, 01, 10 and 11 to the two lowest order address bits on successive clock pulses. The sequence always begin with the base address which is the external address held in the address register.
The address burst logic in a typical synchronous SRAM consists of a binary counter and exclusive-OR gates. For 2-bit burst logic, the internal burst address sequence is formed by the base address bits A2 to A14 plus the two burst address bits A0' and A1'".
I can see that the four possible states (assuming that A0 and A1 are both 0, LOW) will be sequentially added to the external base address, but what is the point of that? I didn't see where did it say it. It says "this allows the memory to read or write at up to four locations using a single address", but what is the advantage of that?
How do they do if they only need to write or read in only a memory location?
Attached the two images.
Attachments
Last edited: