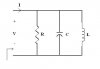
For parallel circuits:
Does a inductor have conductance?
Does a inductor have Susceptance?
Does a inductor have Admittance?
Does a Capacitor have conductance?
Does a Capacitor have Susceptance?
Does a Capacitor have Admittance?
Why is conductance,susceptance,admittance only for parrallel circuit and not for series circuits ?
Is conductance,susceptance,admittance frequency based?
What does conductance,susceptance,admittance do really?
Does a inductor have conductance?
Does a inductor have Susceptance?
Does a inductor have Admittance?
Does a Capacitor have conductance?
Does a Capacitor have Susceptance?
Does a Capacitor have Admittance?
Why is conductance,susceptance,admittance only for parrallel circuit and not for series circuits ?
Is conductance,susceptance,admittance frequency based?
What does conductance,susceptance,admittance do really?